
Fluid biomarkers are an area of active investigation in multiple sclerosis. A leading candidate, neurofilament light chain (NfL), is released with neuroaxonal injury and may represent a marker of disease activity, disease progression, and treatment response. Exactly how NfL might be used in clinical practice and for patient selection in clinical trials remain under investigation, and data from MS Ocrevus pivotal studies may help generate such insights. Importantly, OMNI-BD is also leading analysis of the impact of Ocrevus on circulating B cells and B cell subsets, which has implications for identifying the right dose of the drug for MS patient. In addition, CSF biomarkers may offer complimentary information about inflammatory disease activity and glial activity in MS. OBOE is a dedicated exploratory biomarker study that investigates the role of such soluble CSF markers before and following ocrelizumab treatment. In addition to these cornerstone biomarker studies in MS, next-generation biomarkers are being investigated in ongoing clinical trials of ocrelizumab and fenebrutinib, as well as in studies of real-world MS patients as part of the PHC Floodlight MS Program.
NfL Study Design in the OPERA I & II and ORATORIO studies of Ocrevus
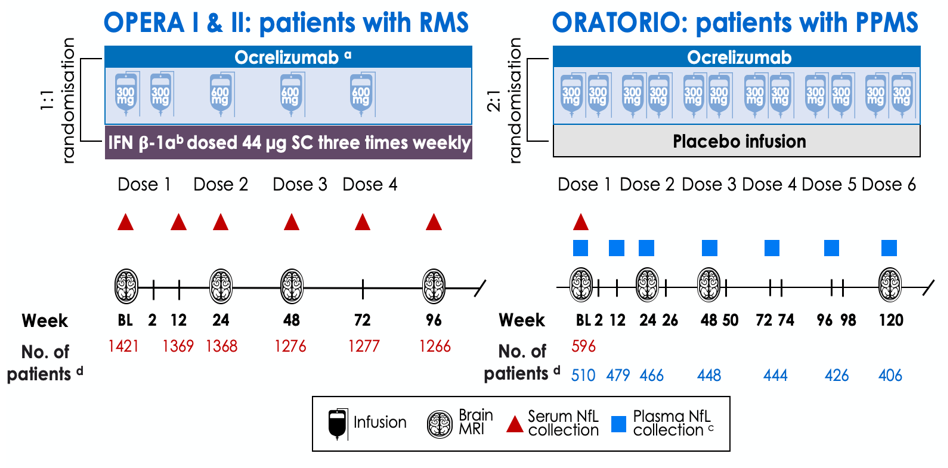
Blood NfL was collected at baseline and post-baseline time points in the OPERA I & II and ORATORIO studies of RMS and PPMS respectively.
Baseline NfL distributions in OPERA (RMS), ORATORIO (PPMS), and healthy donors
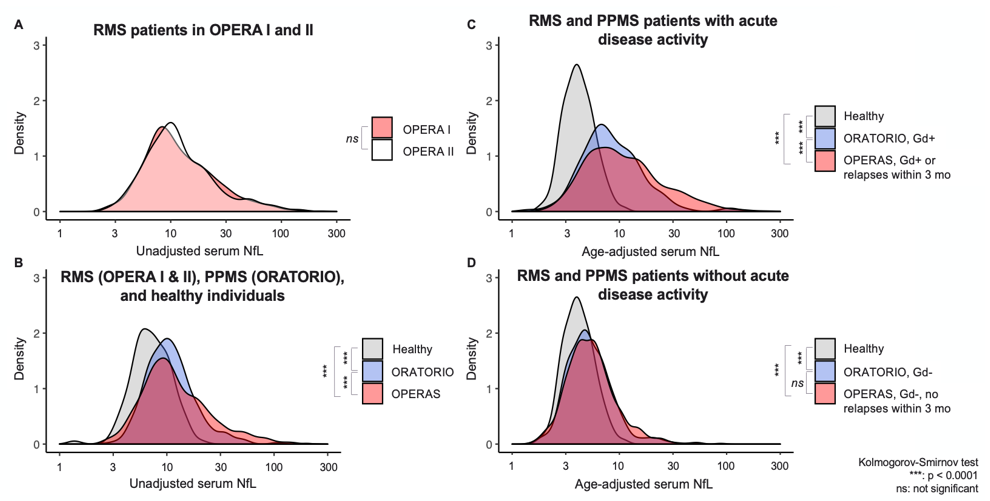
Serum NfL levels are equivalent in the two RMS twin studies (A), are elevated in RMS and PPMS patients compared to healthy donors (B), are especially elevated in MS patients with acute disease activity (C), and show a subtle but equal elevation in RMS and PPMS patients in the absence of disease activity (D). The last observation is consistent with the notion that insidious neuroaxonal injury occurs throughout the disease spectrum.
NfL reduction to following treatment with ocrelizumab
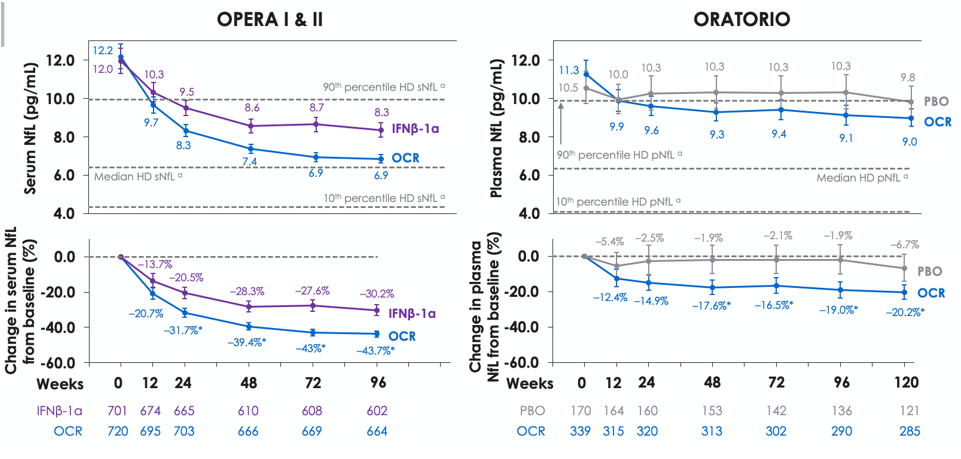
Blood NfL absolute levels (top) and relative change from baseline (bottom) during the controlled treatment in OPERA I and II (left) and ORATORIO (right). NfL levels were significantly reduced following treatment with ocrelizumab in patients with RMS and patients with PPMS, both vs comparator treatment and vs baseline levels.
Baseline NfL levels and impact on disease outcomes
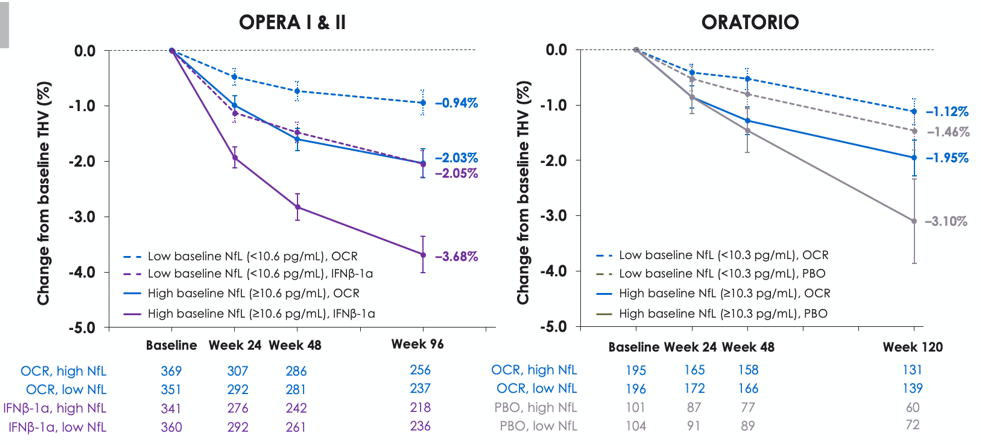
A greater reduction in THV was observed at the end of the controlled treatment period in patients with high baseline NfL (above median, solid lines) compared with low baseline NfL (below median, dotted lines). Figure indicates the relationship between baseline serum NfL and thalamic volume (THV) reduction during the controlled treatment period in each treatment arm of OPERA I and II and ORATORIO.
Impact of ocrelizumab on B-cell subsets
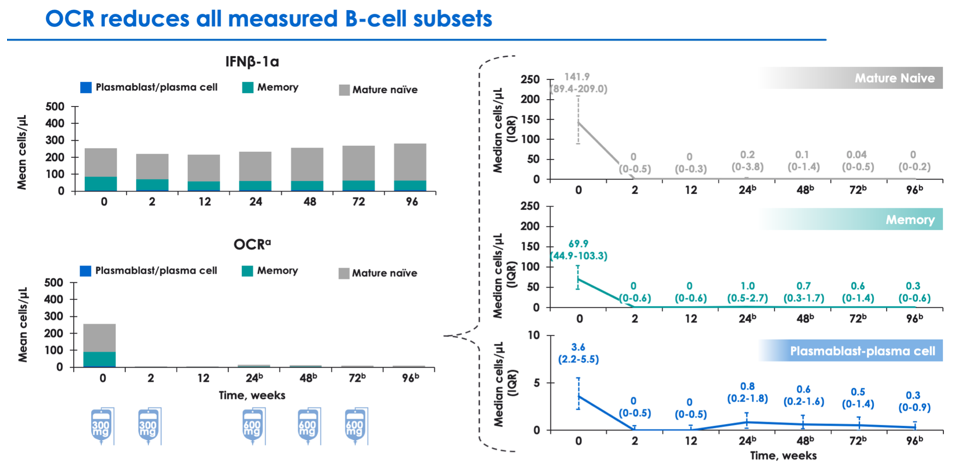
Analyses are ongoing to understand the impact of anti-CD20 therapy on specific B cell populations, including mature naive, memory, and plasmablast-plasma cells. Ocrevus appears to affect robust clearance of mature naive and memory B cells, with relatively lesser impact on plasmablast-plasma cells (which may not express CD20).
Ocrelizumab Biomarker Outcomes Evaluation (OBOE) study design
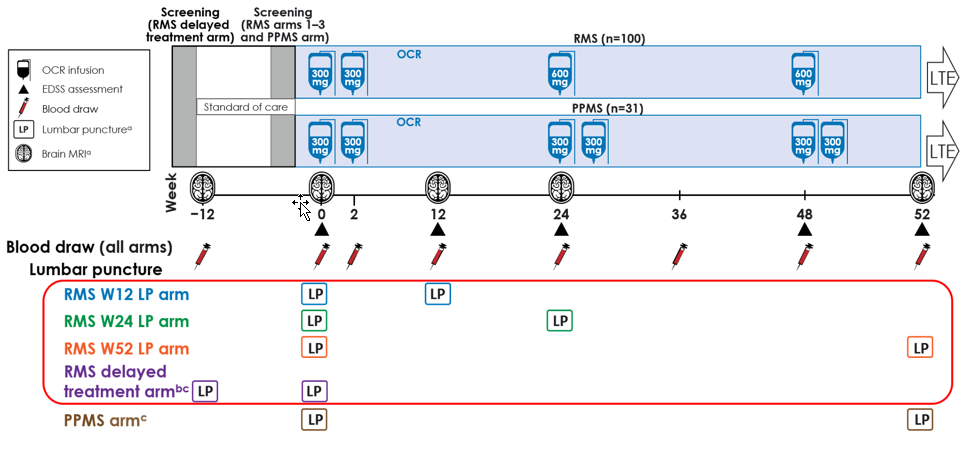
OBOE investigated CSF biomarkers in 100 patients with RMS and 31 patients with PPMS before and following treatment with Ocrevus.
Association of baseline CSF biomarkers with MS disease measures
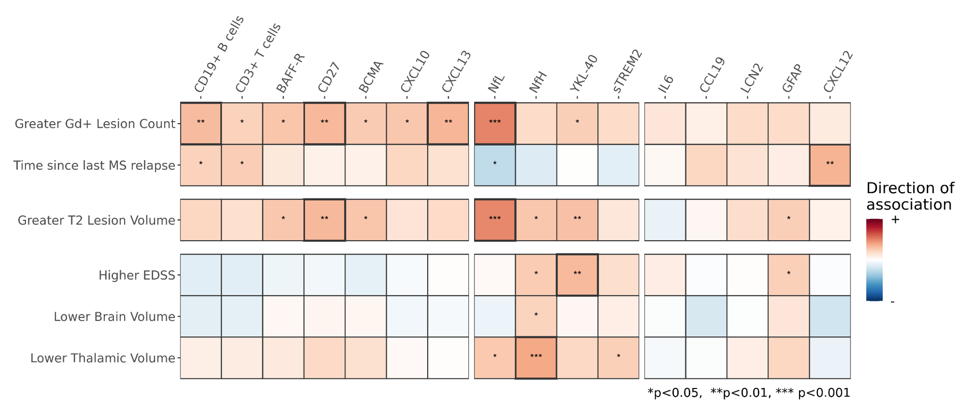
Baseline CSF biomarkers (data for RMS patients shown) are associated with MS disease activity (gadolinium-enhancing lesions), disease burden (T2 lesion volume), and disease severity (EDSS, brain and thalamic volume).
CSF primary endpoint biomarkers are reduced with ocrelizumab treatment
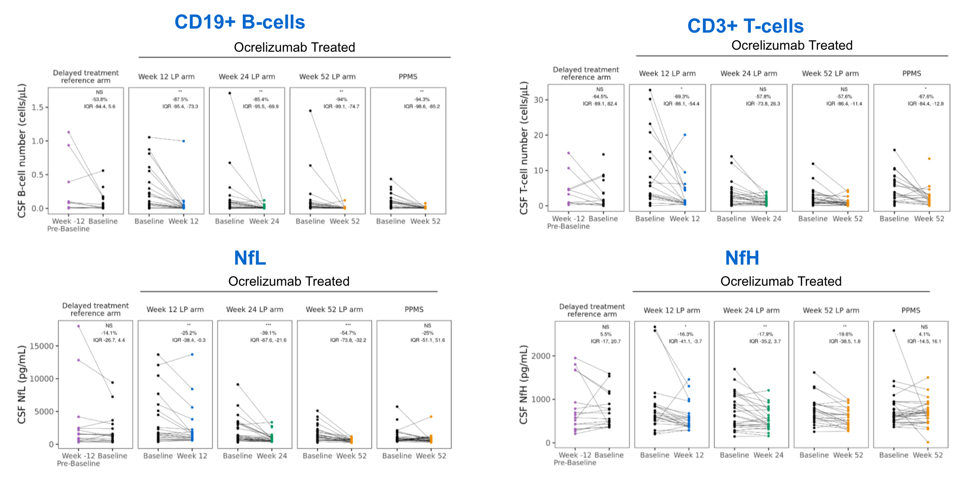
OBOE primary endpoint biomarkers (CSF CD19+ B cells, CD3+ T cells, and NfL) are significantly reduced following ocrelizumab treatment, highlighting its impact on central circulating lymphocyte populations and neuroaxonal injury.
CSF biomarkers of lymphocyte and glial activity are reduced following ocrelizumab treatment
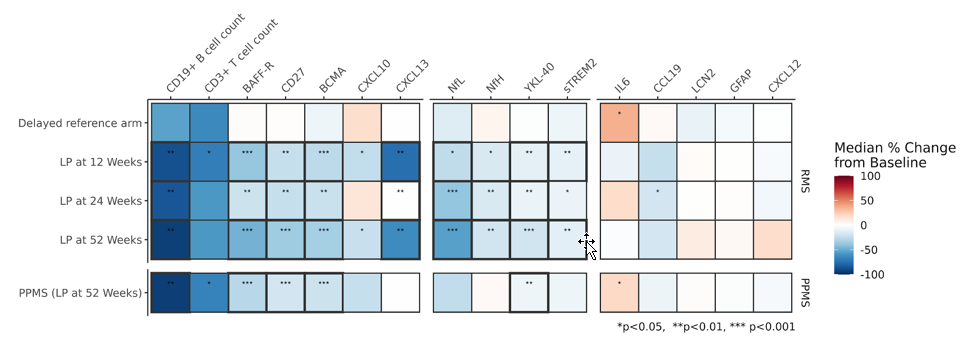
CSF cellular and soluble biomarkers, including primary outcomes (CSF B and T cell levels, CSF NfL), are significantly reduced following treatment of ocrelizumab. This reflects a focused impact on B and T cell lymphocyte populations, but also a broader impact on reduced neuroaxonal injury (NfL, NfH) and glial activity (sTREM2, YKL-40).